- Questions
- Header Files
- Data Types
- Rules for constructing variable and character constant
- Delimiters
- Operators
- Decision Statement
QUESTIONS:-
- Write a program to find sum of 2 numbers.
- Write a program to find difference of 2 numbers.
- Write a program to find sum, difference, product, division, mod of two numbers.
- Write a program to find Simple Interest.
- Write a program to find perimeter and area of a rectangle.
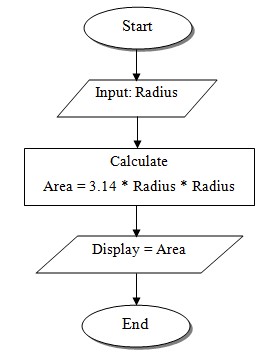
- Write a program to find circumference and area of a circle.
- Write a program to find average of 3 numbers.
- Write a program to calculate sum of 5 subjects and print percentage.
- Write a program to swap two numbers.
- Write a program to swap two numbers without using third variable.
- Write a program to print square of a given number.
- Write a program to print size occupied by different data types.
- HEADER FILES:- In C, header files contain the set of predefined standard library functions. The "#include" preprocessing directive is used to include the header files with ".h" extension in the program.
- stdio.h :- Input/Output function
- conio.h :- Console Input/Output functions
- stdlib.h:- General utility functions
- math.h :- Mathematical functions
- string.h :- String functions
- time.h :- Date and time functions
- limits.h :- size of basic types
- DATA TYPES:-
- RULES FOR CONSTRUCTING VARIABLE AND CHARACTER CONSTANT:-
- A character constant is a single alphabet, a single digit or a single special symbol enclosed within single inverted commas. Both the inverted commas should point to the left.
- The maximum length of a character constant can be 1 character. Ex: 'A' , 'I' , '5' , '='.
Rules for constructing VARIABLE NAMES:-
In C language, any user defined variable name is called identifier. This may be variable names, function names, goto label name, any other data type like structure, union,enum names or typedef name.
- A variable name is any combination of 1 to 31 alphabets, digits or underscores. Some compilers allow variable names up to 247 characters.
- The first character in the variable name must be an alphabet or underscore.
- No special symbol other than an underscore (as in gross_sal) can be used in a variable name. Ex:- rate, time, si_int, m_hra, bas_sal, etc.
- Keywords should not be used as variable names because if we do so, we are trying to assign a new meaning to the keyword, which is not allowed by the computer.
- DELIMITERS:-
- : Colon :- Useful for label
- ; Semicolon :- Terminates the statement
- ( ) Parentheses :- Used in expression and function
- [ ] Square Bracket :- Used for array declaration
- { } Curly Brace :- Scope of the statement
- # Hash :- Preprocessor directive
- , Comma :- Variable separator
- OPERATORS:-
- Arithmetic Operator:- +,-,*,/,%
- Unary Operator:- ++,--,&
- Relational Operator:- >,<,>=,<=,==,!=
- Logical Operator:- &&,||,!
- Assignment Operator:- =
- Conditional Operator:- ?:
- Bitwise Operator:- >>,<<,&,|,^,~
- DECISION STATEMENT:-
- If-else statement
- Nested if-else statement
- Break Statement
- Continue Statement
- Goto Statement
- Switch() statement
- Nested switch() case
- Switch case() and Nested if

0 Comments